In the beginning before "ETW", there were these WMI GUID's... in Windows 2000.
Applies to: Windows 2000
I thought this was interesting, going back to Windows 2000, and how “ETW” worked back then.
Note: Logman wasn't around.
Note 2: Windows Performance Toolkit (WPT a.k.a. xperf/xperfview) wasn't around and it will not work.
927229 Windows 2000 Resource Kit Tools for administrative tasks
https://support.microsoft.com?id=927229
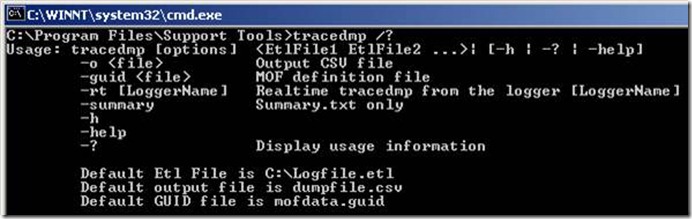
· Trace Dump (tracedmp.exe) : This command-line tool produces a summary of event trace-log data. TraceLog does not produce output that is readable without using an additional tool. TraceDmp functions like a Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) consumer. It takes TraceLog output and parses it into readable form. TraceDmp can also poll real-time trace-buffer data and convert the data to a .csv file. To download this tool, click the following link:
https://download.microsoft.com/download/win2000platform/tracedmp/1.00.0.1/NT5/EN-US/tracedmp_setup.exe
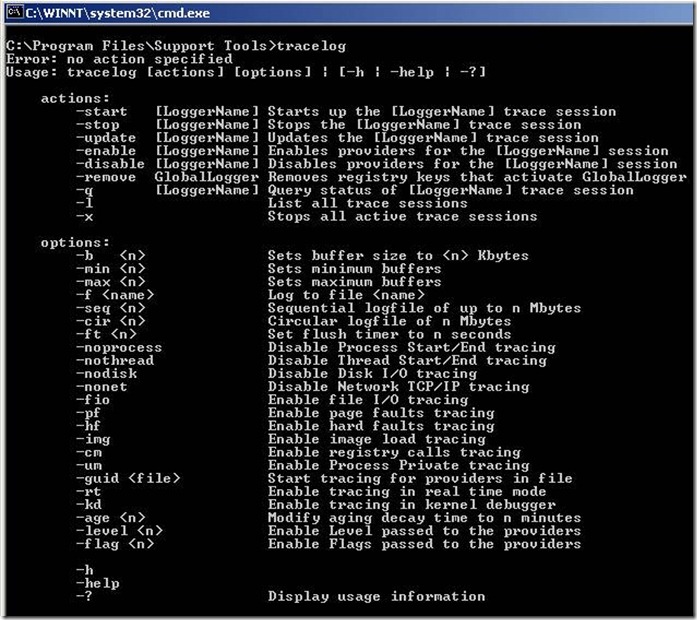
· Trace Log (tracelog.exe) : This command-line tool starts, stops, or enables trace logging. The results of event logging can be viewed by using either the TraceDmp tool or Reducer tool. To download this tool, click the following link:
https://download.microsoft.com/download/win2000platform/tracelog/1.00.0.1/NT5/EN-US/tracelog_setup.exe
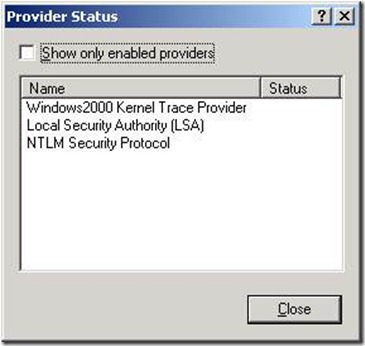
// These are the built-in providers for Windows 2000.
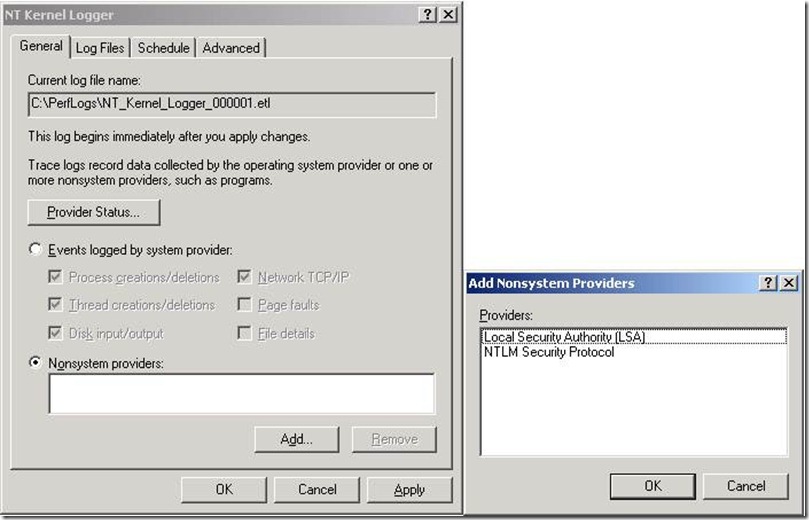
Yeap, three (3) of them.
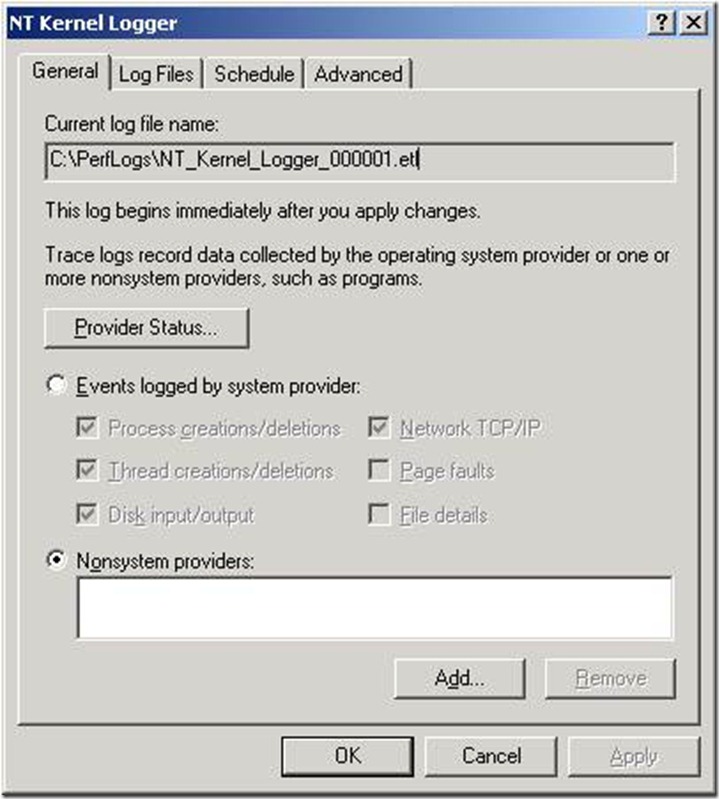
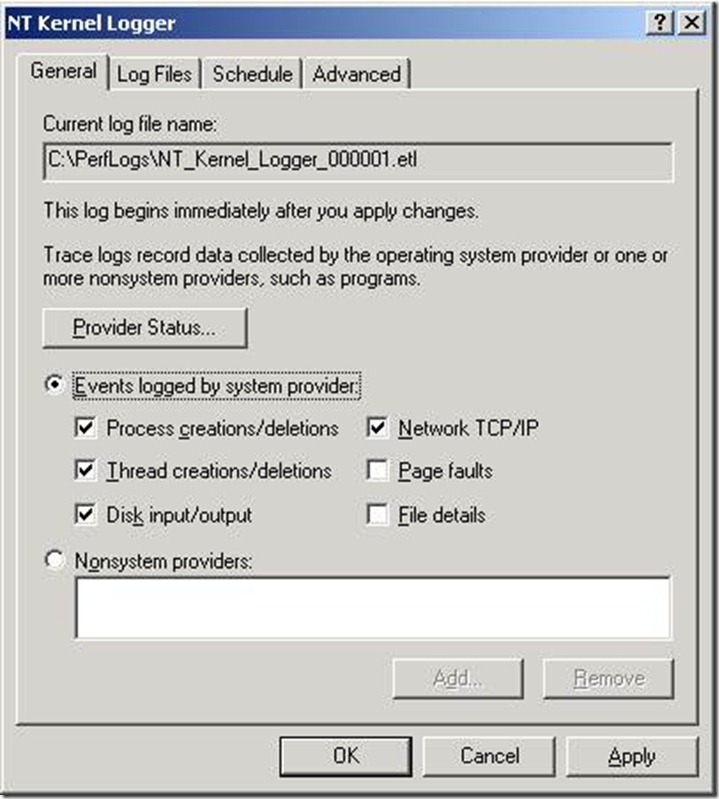
And we could see that we had the following six (6) kernel loggers:
Process creations/deletions
Thread creations/deletions
Disk input/output
Network TCP/IP
Page faults
File details.
// These are the user mode providers, just two (2) of them.
More to come about ETW on my next posts.