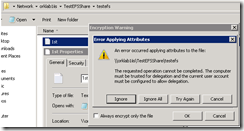
Remote Encryption yaparken "An error occurred applying attributes to the file:"(File Path)"The requested operation cannot be completed. The computer must be trusted for delegation and the current user account must be configured to allow dele
Bir share üzerinde bulunan bir dosya encrypt edilmek istenildiginde : "An error occurred applying attributes to the file:"(File Path)"The requested operation cannot be completed. The computer must be trusted for delegation and the current user account must be configured to allow delegation." uyarisi aliniyor ve encryption tamamlanilamiyor.
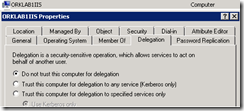
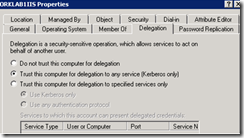
Bu islemi delegation olmayan bir sistemde (ORKLAB1IIS)
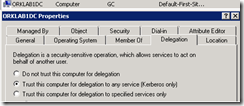
Ve delegation olan bir sistemde (ORKLAB1DC) denedim.
Delagation olmayan sistemde EFS denedigimde (ORKLAB1IIS) bu durumu gözlemledim.
Fakat delegation olan sistemde (ORKLAB1DC) bu islemi yaptigimda
Dolayisiyla EFS yapilacak Network Share’lerin oldugu sistemlerde “Trust this computer for delegation to any service (Kerberos only) seçeneginin seçilmesi gerekmekte.
Delagation olmayan sistemde EFS denedigimde (ORKLAB1IIS) , delagation’i enable ettigimde gene ayni hatayi aldim.
Dolayisiyla bu islem için önce AD tarafinda replication’I tetikledim
repadmin /syncall /eAPd
repadmin /syncall with the /A(ll partitions) P(ush) e(nterprise, cross sites) d(istinguished names)
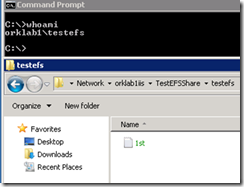
sonrasinda da tekrar test kullanicim ile login oldum
Bu islem sonrasi artik bu sharedeki kaynagi encrypt edebildim.
Peki Delagation ne yapar ? Bu durum ile ilgili en basit olarak buldugum kaynak asagidaki kaynak ama yarin daha fazla arastirma ile size geri dönüs yapacagim.
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc782684(v=ws.10).aspx
Description
This security setting determines which users can set the Trusted for Delegation setting on a user or computer object.
The user or object that is granted this privilege must have write access to the account control flags on the user or computer object. A server process running on a computer (or under a user context) that is trusted for delegation can access resources on another computer using delegated credentials of a client, as long as the client account does not have the Account cannot be delegated account control flag set.
This user right is defined in the Default Domain Controller Group Policy object (GPO) and in the local security policy of workstations and servers.
Caution
• Misuse of this user right, or of the Trusted for Delegation setting, could make the network vulnerable to sophisticated attacks using Trojan horse programs that impersonate incoming clients and use their credentials to gain access to network resources.
Ayrica edindigim asagidaki bilgide oldugu gibi trusted for delegation devre disida olsa legacy OS ‘lerden encrypt islemi yapilabiliyor. Bu durumu test etme sansim olmadi ama test etmemizi gerektirecek bir durumda bulunmuyor. Zira artik bu isletim sistemleri çok fazlaca kullanilmamakla birlikte artik yeni jenerasyon isletim sistemleri kullanilmakta.
Trusted for delegation is failing for EFS when a Vista client tries to encrypt on a WS2003 SRV in a LH domain. When the LH DC is at the Longhorn domain functional level, users who are logged onto a Vista/LH client cannot access previously-encrypted files on the downlevel server and cannot encrypt new files on the server.
Note:
1. In this same domain environment, users who are logged onto a Windows XP client can encrypt and decrypt files on the same server.
2. The algorithm change made is causing this issue for Vista/LH clients.
Delegation ile ilgili daha fazla bilgiyi asagidaki linkten edinebilirsiniz :
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc739740(v=ws.10).aspx
Delegation is the act of allowing a service to impersonate a user account or computer account in order to access resources throughout the network. When a service is trusted for delegation, that service can impersonate a user to use other network services.
Ayrica asagidaki bilgi MS Press ürünü olan Windows Server 2008 PKI and Certificate Security kitabinda yazilmaktadir.
Remote Encryption
The EFS encryption process changes when you attempt to encrypt a file on a remote server.
The process used by Windows 2000 and Windows XP clients is different from the new
process implemented for Windows Vista clients.
Remote EFS Encryption for Windows 2000 and Windows XP Clients
When you perform remote file encryption from a Windows 2000 or Windows XP client using
Server Message Block (SMB) or Common Internet File System (CIFS), the file is encrypted
at a remote file server in a share created on the file server. Encryption is performed by allowing
the remote file server to impersonate the user.
Important The computer account of the remote file server must have the Trusted For
Delegation option enabled for its computer object in AD DS. This allows the computer
to impersonate any user through Kerberos delegation. For this reason, many organizations
consider enabling the Trusted for Delegation option a huge security risk.
When the computer account impersonates a user, it loads a user profile for the user account
on the local file system and follows the same process to determine whether an EFS certificate
exists for the user account. A different EFS encryption certificate is implemented at each file
server where EFS encryption is enabled. In fact, the remote EFS encryption certificates are
different that the EFS certificate used for local EFS encryption.
Important The same process is used by a Windows Vista client when it connects to a share
hosted on a server computer running Windows 2000 Server or Windows Server 2003.
An alternative to allowing EFS encryption on file servers is to implement Web-based
Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV), or Web folders, at the remote file server.
Rather than connecting to the file server on TCP port 445 (or TCP port 139 for the older SMB
protocol), the server allows connections through the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
port, TCP port 80 (or TCP port 443 if Secure Sockets Layer [SSL] is implemented).
The benefit of using WebDAV is that a Windows XP client performs file encryption on the
local computer rather than the remote file server. This provides better data protection as
the file is transmitted from the client’s computer to the remote file server.
When a Windows XP client connects to a WebDAV access point on a remote server, files are
encrypted locally on the client and then sent to the WebDAV server as an encrypted file using
an HTTP PUT command.
Likewise, when a Windows XP client connects to the WebDAV access point to open a
previously encrypted file, the encrypted file is transmitted to the Windows XP client via an
HTTP GET command and then decrypted locally on the client.