L2TP VPN issues when utilizing TMG as your RRAS server and NLB is configured on your external Interfaces
Hello All! It’s Brett Crane from the Forefront Edge team here at Microsoft. I wanted to take a few moments to talk about an issue you may see in your RRAS environment if you are utilizing NLB to load balance your External Interfaces of your TMG Array and you’re using an IPSec based Method.
Here is a problem statement you may be facing:
“My VPN clients are failing to connect to my environment when utilizing L2TP and connecting to the Virtual IP of the Array. If I connect to the physical IP of either of the nodes it connects without issue. PPTP and SSTP work but for some reason L2TP doesn’t. I am positive I have it setup right. What could be wrong with TMG or RRAS?”
Well, I will start by saying that if you are seeing this you may have already pulled out all your hair! There’s nothing in the event logs what-so-ever pointing to an issue of any kind! As well… when you do live tracing in TMG to see why the VPN connection is failing everything seems to be working fine. Where do you start looking for data???
Based on the issue I’m covering I’ve found that Network Monitor is a very useful tool to help troubleshoot LT2P/IPSec related issues. In addition, if you have a TMG Array with Integrated NLB enabled on the External Network, I’d suggest that you install Network Monitor on all nodes of the array as you may not be sure which node will handle the L2TP/IPSec traffic in question.
* You can download the most recent version of Network Monitor from the following location: http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=4865
Once Network Monitor is installed and running, go ahead and reproduce the L2TP VPN client connection issue. Once you have reproduced your issue stop your tracing and apply the following Display Filter: IKE or ESP. This will cause Network Monitor to show you IPSec related data.
Looking through the trace you will see the following behaviors…
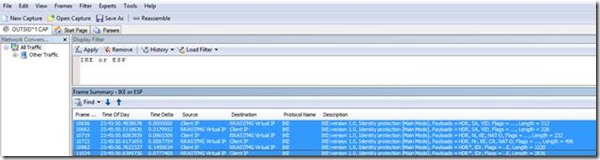
The client tries to setup an IPSec Tunnel with the RRAS\TMG Server’s Virtual IP Address (Keep in mind that the Microsoft L2TP protocol utilizes IPSec as an underlying security protocol) . The first part of the IPSec process is what we call Main Mode. As you can see below this works fine:
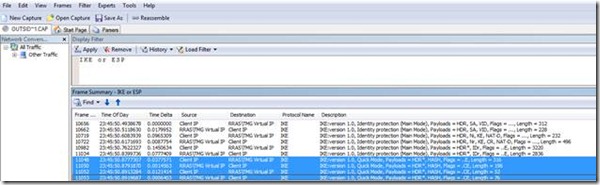
The next thing we see is that the Quick Mode Process works without issue. Quick mode is the second part of the communication process the IKE protocol utilizes to setup an IPSec Tunnel:
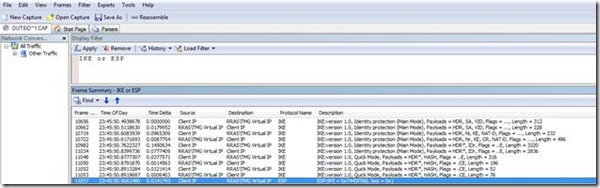
Once Main Mode and Quick Mode have completed we will now have an IPSec tunnel created and the client will communicate through that tunnel utilizing the ESP protocol:
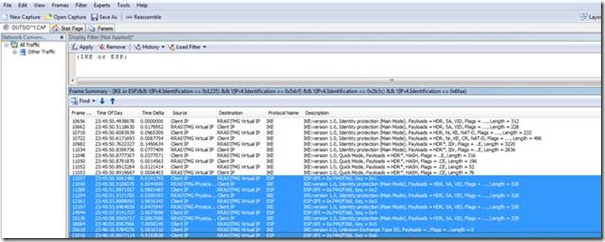
Now comes the odd part. Instead of the Server returning ESP communications to the Client, as it should, it tries to open a new tunnel up to the client. It does this via a new Main Mode connection over the physical IP Address on the External interface of the RRAS\TMG server instead of the Virtual IP. The client would not have a policy to support this process therefore it silently drops the requests and retransmits the ESP data it sent before. Each time the server receives the ESP data it tries to send out a Main Mode request. The behavior can be seen below:
So the question is…
“Why does the server try to create a new tunnel out to the client over the Physical IP while there is already a tunnel established over the Virtual IP address?”
Answer…
The problem is that the server is not selecting the correct IPSec Security Association (SA) when trying to communicate back. Therefore it tries to create a new one. The only way the server sees to connect up to the clients IP Address is by sending the data out of its Default Gateway which is associated with its Physical IP Address\NIC.
How do I resolve this…
This is a known issue in the Server 2008 R2 operating system. To resolve this issue all you need to do is connect to the Microsoft TechNet article below and choose the “View and request hotfix downloads” Link in the upper Left corner.
You cannot establish an IPsec tunnel to a computer that is running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 through a NAT device
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;2523881
* Again… keep in mind that the data in the article only refers to IPSec and you are using L2TP. That’s perfectly ok. That’s because L2TP uses IPSec as its means of creating a secure tunnel. As well, the information covered in the article also covers NAT-T configurations. That is only 1 scenario that was found. The fix actually covers multiple scenarios although not listed.
Thank you for your time in reading this post. I hope it helps you out!
Author:
Brett Crane
Security Support Escalation Engineer
Microsoft CSS Forefront Security Edge Team
Technical Reviewer:
Richard Barker
Security Sr. Support Escalation Engineer
Microsoft CSS Forefront Security Edge Team