Understanding a scenario where TMG drops the packet as spoofed even when the source IP doesn’t belong to the internal network
1. Introduction
The core TMG behavior (which is the same on ISA) for handling spoofed packets is well known. Basically, if the IP address belongs to the internal network and it is received on the external interface, it is expected that the packet will be dropped. By definition, the intrusion detection system on TMG will do the following:
Inspect · The IP address is included in the IP address ranges assigned to the network of the network adapter through which it was received. · The routing table indicates that traffic destined to that address can be routed through a network adapter belonging to that network. If the source IP address of a packet is not considered valid, Forefront TMG drops the packet and generates an event that can trigger an IP Spoofing alert. From: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc995155.aspx |
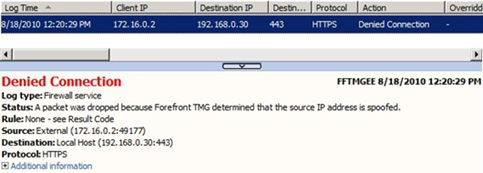
This post describes a scenario where the external user was trying to access OWA published through TMG 2010 and the request was timing out. From the TMG side, it was possible to see that the traffic was getting denied as spoofed, as shown in the log below:
Note: if you to the logs for this traffic, you will see that it drops the packet for the following reason: FWX_E_FWE_SPOOFING_PACKET_DROPPED .
2. Troubleshooting
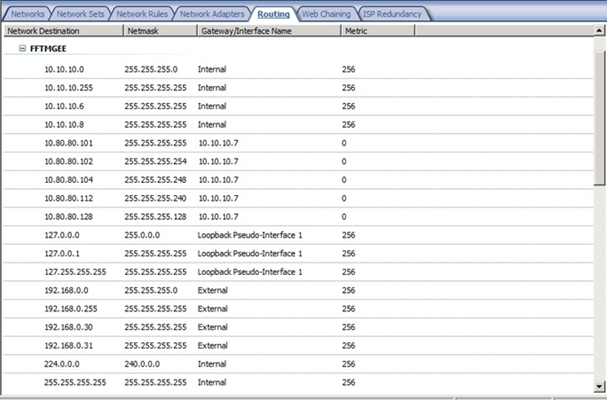
When you receive spoofing error, the first action that you should take is to make sure that your network definition is correct. In other words, make sure that the source address (in this case 172.16.0.2) does not belong to your internal network. For this particular example that we are using on this post, TMG didn’t have this range as part of the internal network as shown below:
Notice that we have internal, external and also the 10.80.80.0/24 network, which is the VPN Client network, but 172.16.0.0/16 is not part of the internal network. So, why TMG is blocking the traffic as spoof?
The reason why this happens is because TMG analyzes the source IP of the packet and verify if this network is reachable via external interface (where it was received), if it is not then it interprets this traffic as spoofed. A snip from the lower level TMG tracing shows the following:
ERROR:GetBestRoute2(ip=172.16.0.2) failed 0xc000023c(STATUS_NETWORK_UNREACHABLE) Info:recv packet will be considered spoofed, reason : source address not routable thru recv interface Warning:Dropping packet - FWE_SPOOFING Info:source=172.16.0.2:49177 dest=192.168.0.30:443 protocol=6 action =DROP Info:Filter hook denied the packet Info:Stopping inspection actions! We did not get a permit |
This problem was fixed by adding a default gateway on the external network of TMG. If you can’t add (for some network infrastructure reason) a default gateway on the external adapter of TMG, you will need to manually add a route to the network that it is getting dropped as spoofed so TMG knows how to get there.
3. Conclusion
This post explains a scenario where a missing element on the configuration (default gateway on the external interface) caused legitimate traffic to be denied as spoofed. Keep in mind those rules of thumb while configuring TMG networks so that you can avoid issues of this nature.
Author
Yuri Diogenes
Sr. Security Support Escalation Engineer
Microsoft CSS Forefront Security Edge Team
Technical Reviewers
Mohit Kumar
Sr. Security Support Escalation Engineer
Microsoft CSS Forefront Security Edge Team
Thomas Detzner
Escalation Engineer
Microsoft CSS Forefront Security Edge Team