The Management Server
 Part of evaluating Windows Essential Business Server 2008 is about understanding how it all fits together. As you hopefully know by now Essential Business Server 2008 runs on three Servers. Today we’re going to cover what is actually installed on the management server and explain a little about its purpose.
Part of evaluating Windows Essential Business Server 2008 is about understanding how it all fits together. As you hopefully know by now Essential Business Server 2008 runs on three Servers. Today we’re going to cover what is actually installed on the management server and explain a little about its purpose.
The Management Server is the workhorse of the Windows Essential Business Server 2008 solution and is the first server installed during deployment. It hosts the Administration Console which is the management center for most Windows Essential Business Server 2008 administration tasks. The Management Server also provides the majority of the core infrastructure services for Windows Essential Business Server 2008. This includes Active Directory Certificate Services (AD-CS), Active Directory Domain Services (AD-DS), Domain Name System (DNS), and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
In a Windows Essential Business Server 2008 solution, the Management Server is vital to helping ensure the overall health and security. It includes Microsoft System Center Essentials (SCE) 2007 for monitoring and reporting on connected devices. The Management Server also includes Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to help ensure your Windows-based server and desktop computers are always up-to-date. SCE also enables the updating of 3rd party applications as well.
Primary Management Server Services
· Active Directory Domain Services – Provides central authentication and authorization services. The Management Server holds most Active Directory Domain Services roles;
· Active Directory Certificate Services – Manages X.509 certificates for protocols such as S/MIME and Secure Socket Layers (SSL);
· Domain Name System (DNS) – Provides the foundation for Active Directory Domain Services and translates host names to IP addresses for network access;
· Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) – Service used by computers on a network to obtain IP addresses and other parameters, such as the default gateway, subnet mask, and IP addresses of DNS servers from a DHCP server;
· Print Services – Provides sharing and management for printing and imaging devices;
· System Center Essentials 2007 – Offers proactive monitoring for Windows-based computers, applications, and devices. Provides update management, software deployment, hardware and software inventorying, and comprehensive reporting;
· SQL Server Express 2005 – Data repository for Systems Center Essentials 2007;
· Terminal Services – Allows administrators to remotely access the server;
· Web Services (Internet Information Services) – Web server providing services for System Center Essentials 2007 reporting and Windows Update Services;
· Licensing – Enables management and compliance reporting for Windows Essential Business Server 2008 Client Access Licenses; and
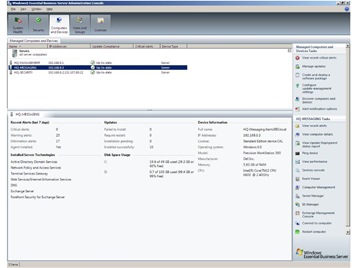
· Windows Essential Business Server Administration Console – (The CROWN jewel of the EBS experience, we’re going to cover that more in later blog posts) offers insight into an organization’s overall health, security, and operational status. The console is also extensible, providing the ability for other Microsoft products or third-party providers to add management capabilities to the Administration Console’s interface.
There are some other noteworthy elements. First up, with the power of Terminal Services Remote App, you’re able to access the administration console from any machine, albeit another server, or even you RDP client enabled client PC. Also in some configurations, you can manage SharePoint, AV, and Backup Services from Microsoft and other 3rd party vendors thought the console’s extensible UI.
All of this is deployed to best practice around specific considerations, such as security, manageability and performance. One of the goals around creating each of these role servers is to increase your server density, whilst taking a considered view on what is the right technical configuration for a site with under 300 desktops.