磁碟右鍵內容與開啟磁碟點選所有檔案右鍵內容檔案大小不一致
磁碟機右鍵內容
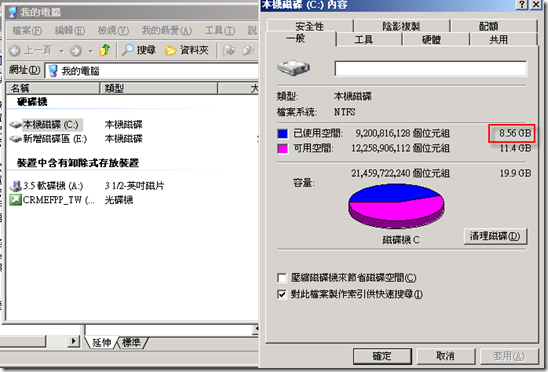
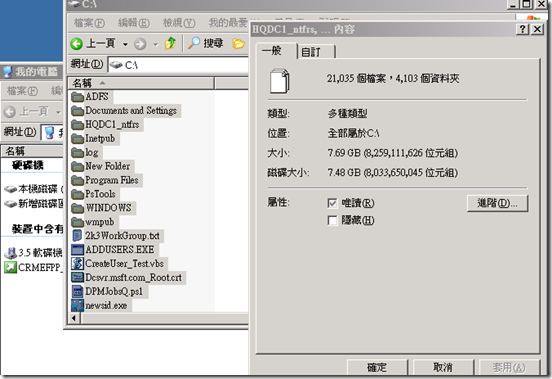
進入到磁碟機後全選包含隱藏檔案右鍵內容所看到的檔案大小不一致
Technical Background
==================
1. Usually, our customer use Explorer to get disk space usage information. For example, select all the folders and then click Properties. It shows the space being used by those folders. However, the value shows in the size on disk cannot reflect the real disk space usage.
Here are the common reasons why some disk space usage is not counted by explorer.
a. Explorer will not count the folder/file which the logon user does not have permission to access.
b. Hidden folder/files are not counted if Show hidden and system files is not selected in Folder Option.
c. Explorer will not count file’s second data attribute (or in some document, we called it alternative data stream). In NTFS file system, everything is an attribute. File’s data is also an attribute. By default, one file has one data attribute, but we can create multiple data attribute for one file.
d. Explorer does not count the disk space being used by file system metadata file like $MFT, $Secure.
$MFT contains all the file records. Each file record is 1K. NTFS use at least one file record to describe a file or a folder. NTFS will not shrink the $MFT file size. If huge amount of files have ever been created, even if the files are deleted later, the size of $Mft could be very large with lot of unused file records.
$Secure is a NTFS metadata file which contains all the security descriptors (NTFS permission) and necessary indexes for the security descriptor and its hash value. Each security descriptor will have a corresponding ID (security ID). In each file record, it has the security ID. NTFS gets the security ID and find the corresponding security descriptor for a particular file or folder.
2. In the NTFS file system level, there are three additional reasons which will cause the disk space usage is more than what customer expects.
a. File system corruption. Some free disk space are incorrectly marked as allocated which will cause unexpected disk space usage.
b. Reserved disk space. NTFS driver could reserve clusters for specific purpose. One typical situation is: If a NTFS compressed file is opened as memory mapping file, NTFS will reserve additional clusters until the cached data tear down. The reserved clusters will be released after a reboot.
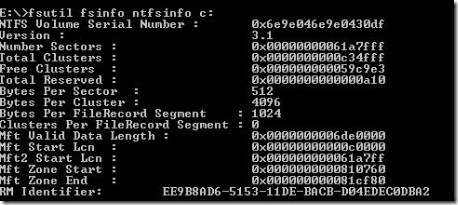
c. Many small files. For file system, the allocation unit is what we called Cluster. Cluster size is 4K in most of the cases (8 sectors). If the disk has many small files which size is like 1K or 2K, NTFS will still allocate one cluster for each file. So, disk space might be wasted. We can run the command line “fsutil fsinfo ntfsinfo <drive letter>” to get the size of cluster. In the sample below, you can see the size of a cluster is 4K.