Step-By-Step: Enabling Hyper-V for use on Windows 10
Virtualization provides a plethora of solutions from making the most of an organization’s hardware investment to running specific applications in other OS offerings. Windows 8 was the first Windows client operating system to include hardware virtualization support natively. Using the same technology found in Windows Server 2012 R2, the embedded Hyper-V client allowed IT professionals to move VMs from server to client without the requirement to re-learn the use of Hyper-V features and tools. Further enhancements were introduced in Windows 8.1 such as Enhanced Session Mode, enabling high fidelity graphics for connections to VM's using the RDP protocol, and USB redirection which is enabled from the host to VM's.
Windows 10 brings further enhancements to the native hypervisor offering. These include:
- Hot add and remove for memory and network adapters – works with generation 2 virtual machines running both Windows and Linux
- Windows PowerShell Direct – the ability to run commands inside a virtual machine from the host operating system
- Linux secure boot - Ubuntu 14.04 and later, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 OS offerings running on generation 2 virtual machines are now able to boot with the secure boot option enabled
- Hyper-V Manager Down-level management - Hyper-V manager can manage computers running Hyper-V on Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1
Step 1: Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to successfully run Client Hyper-V on Windows 10:
- Windows 10 Pro or Enterprise 64 bit Operating System
- 64 bit processor with Second Level Address Translation (SLAT)
- 4GB system RAM at minimum
- BIOS-level Hardware Virtualization support
Step 2: Setting Up Hyper-V
- Ensure that hardware virtualization support is turned on in the BIOS settings
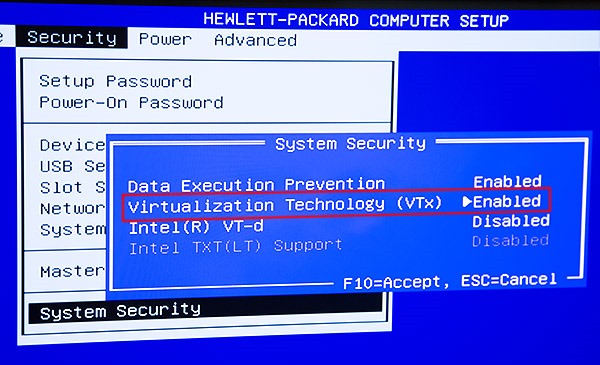
- Save the BIOS settings and boot up the machine normally
- Click the search icon (magnified glass) on the taskbar
- Type turn windows features on or off and select that item
- Select and enable Hyper-V
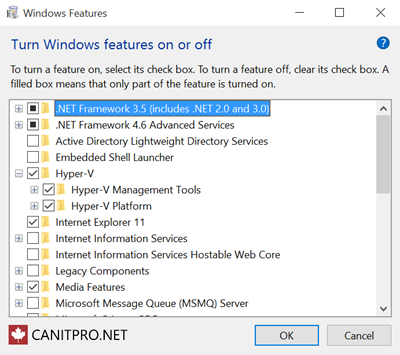
- If Hyper-V was not previously enabled, reboot the machine to apply the change.
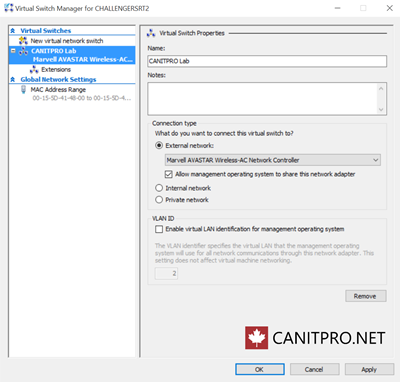
NOTE: As a best practice, configure networking for the Hyper-V environment to support external network connections. Also ensure that a virtual switch has been created and is functional.
- Click the search icon (magnified glass) on the taskbar, type Hyper-V Manager and select the item
NOTE: Right click Hyper-VManager to pin it to the task bar
- Open the Virtual Switch Manager, found on the Actions panel in the Hyper-V Manager, by typing Hyper-V at the Start Screen
- Select Virtual Switch Manager in the Actions pane
- Ensure that External is highlighted, and then click on the Create Virtual Switch button
- If more than one NIC in is present, ensure that the proper NIC is selected for use on the VM external network connections