Step-By-Step: Building a Private Cloud with Hyper-V Server 2012
While attending a flurry of IT Professional user group meetings across Canada, I have spoken to many IT Pros experiencing great success is expanding their compute capacity utilizing Microsoft's enterprise-grade, bare-metal hypervisor solution. Hyper-V Server 2012 offers the same level of scale, clustering, live migration and DR-replication capabilities as the Hyper-V role found in Windows Server 2012, with one small exception, the enterprise hypervisor feature set is FREE. Hyper-V utilizes the VHD virtual hard disk standard for broad industry compatibility. Utilizing said format negates the risk that data will be locked to a proprietary disk format and provides flexibility for growing your organization's Private Cloud compute foundation via a hybrid mix of on-premise hypervisor hosts, public cloud fabric via Windows Azure and/or third-party service providers/hosting partners.
As mentioned Hyper-V Server 2012 is a FREE purpose-built product which includes the core of Windows Server 2012 and Hyper-V. The union of said cores result in a streamlined Type-1 hypervisor optimized for remote management while providing the same virtualization scalability and high availability features found utilizing the Hyper-V role in the full version of Windows Server. These features include:
- Utilizing up to 320 logical processors per Hyper-V host
- Utilizing up to 4TB of physical memory
- Live Migration
- Storage Migration
- Virtual Machine Replication
- Clustering
Microsoft also provides further information regarding specific improvements in Hyper-V Server 2012 over Hyper-V Server 2008 R2 for reference.
Should your organization not need the additional capabilities of Windows Server 2012, utilizing the standalone Hyper-V 2012 server offering may prove cost effective as additional license grants provided by Windows Server 2012 may have been already purchased via your Windows Server licenses and not require an additional purchase. An example for use may include setting up dedicated hosts running only the Hyper-V role for consolidating large numbers of virtual machines on standalone or clustered hosts or setting up a client virtualization/VDI solution leveraging Hyper-V where Windows Server OS licenses are not needed for each VM. In addition, while Hyper-V Server 2012 itself cannot directly support other roles beyond Hyper-V on the parent partition, it can integrate with your existing enterprise Active Directory and/or host virtual machines running the full Windows Server OS that can provide these additional roles.
Getting started with Hyper-V Server 2012
- Review the System Requirements for Hyper-V Server 2012
- Download Hyper-V Server 2012
- Install Hyper-V Server 2012
- Configure drivers (if needed) on Hyper-V Server 2012
- Configure Admin Password, IP Address and Domain for Hyper-V Server 2012
Managing Hyper-V Server 2012
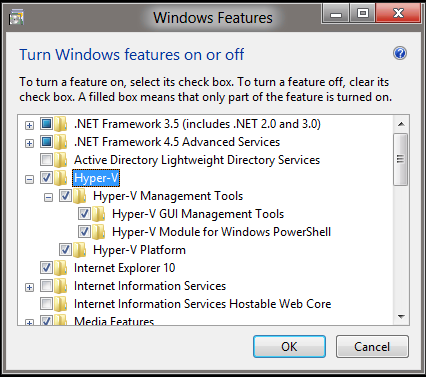
Enable the Hyper-V Management Tools on the management designated Windows 8 machine via Control Panel > Programs and Features > Windows Features
Download and Install the Windows Server 2012 Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) on the management designated Windows 8 or Windows 8 RT tablet or laptop.
Enable Remote Management on Hyper-V Server 2012
Manage Hyper-V Server 2012
Learn more regarding Hyper-V 2012 and have a chance in winning your own lab computer by participating in the free Microsoft offered Virtual Academy. Complete two TechNet evaluations, and take the selected Microsoft Virtual Academy courses for your chance at a $5,000 grand prize or a chance to win an HP EliteBook Revolve and two chances to win 400 Microsoft Points.