KMS Count is not increasing
Today’s blog will cover KMS volume activation and the KMS count. Many times customers will contact us and report that their KMS count is not as high as they think it should be or it is not increasing.
You may also see the following error message when you try to activate
0xc004f038: The Software Licensing Service reported that the computer could not be activated. The count reported by your Key Management Service (KMS) is insufficient. Please contact your system administrator.
The KMS count minimum is the following to activate KMS clients:
- Windows Vista/Windows 7: 25
- Windows Server 2008/Windows Server 2008R2: 5
Note: The count is a combination of all the machines. For example if you have 4 Windows 7 computers and 1 Windows Server 2008 computer then you have met the minimum count necessary to activate Windows server SKU’S. You would need to get another 20 machines to meet the minimum count for Windows Vista and Windows 7.
Also it is important to remember that the count will max out at either 10 or 50(double the minimum count required of the clients contacting the KMS host). If you only have Windows Vista or Windows 7 KMS clients contacting the KMS host the maximum it would show is 10. If any Windows Server or Windows Server 2008R2 computers contact the host the maximum count will be 50.
There are a number of possible reasons why the count is not at the expected number:
- Duplicate CMID’S
- Rogue” KMS hosts
- Clients using Non-VL keys
- Clients preset to another KMS host
Duplicate CMID’S
This issue is covered in another blog. See https://blogs.technet.com/b/askcore/archive/2009/10/16/kms-host-client-count-not-increasing-due-to-duplicate-cmid-s.aspx
“Rogue” KMS hosts
This is the more common scenario. If a user doesn’t understand the correct usage of the KMS host key and they have the proper permissions they can accidently publish a KMS host to DNS. When this happens you may have some of your clients connecting to this KMS host instead of the authorized KMS host. To verify you can either check DNS for _vlmcs records or run the following command
nslookup -type=all _vlmcs._tcp
Note: There is a space between all and _vlmcs
The resolution is to convert these Rogue KMS hosts back to KMS clients and then remove the DNS record. For more information see https://blogs.technet.com/b/askcore/archive/2009/03/09/kms-error-0xc004c008-activating-client.aspx
One way to prevent this from occurring is to utilize the security permissions on the _vlmcs record to only allow authorized KMS hosts to update it. For more information see the topic “Change the Default DNS Permissions for SRV Records”
Clients Using Non-VL Keys
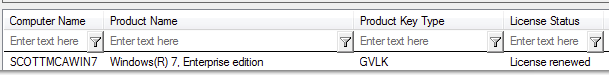
You can use different types of keys to install Windows so you need to make sure that your clients are setup using the KMS Client Setup key and not an OEM, retail, or MAK product key. You can use the VAMT tool or slmgr.vbs /dlv to determine the type of key that was used to setup the computer.
For example in VAMT you should see the computer listed with a Product Key Type of GVLK.
If you run slmgr.vbs /dlv you should see output similar to this:
Description: Windows Operating System - Windows(R) 7, VOLUME_KMSCLIENT channel
Clients preset to another KMS host
If any of the clients have had ‘/skms’ run on it to preset the client to a specific KMS host (authorized or Rogue) then the count on a particular KMS host may not reflect what you believe it should be. Once you run ‘/skms’ the KMS client will only talk to that specific KMS host. To reset the KMS client to use DNS autodiscover you can run ‘/ckms’ on the client to allow it to autodiscover a new KMS host in DNS or you can run ‘/skms’ to point the client to the correct KMS host.
Hope this helps with your KMS troubleshooting.
Scott McArthur
Microsoft Enterprise Platforms Support
Senior Support Escalation Engineer