Windows Server 2008 in the Enterprise an overview
Technorati Tags: Windows Server 2008,Overview,Web,Virtualization,Foundation,Infrastrcuture,Security
By now you have either heard or read something somewhere that Microsoft is about to release a new Serve operating System. The new server operating system is Windows Server 2008, slated for world wide release on February 27 2007. I have now been working with and presenting on Windows Server 2008 for the past one year and the first thing I talk to customers about is why this is a significant release of Window Server Platform, and the top reasons for why they should consider Windows Server 2008 as a important part of their IT Infrastructure platform.
The capabilities the new version of Windows Server brings to an IT infrastructure is a strategic asset and the critical foundation upon which software can deliver services and user applications that a business needs in order to operate effectively and succeed. Windows Server 2008 enables greater business success by providing a platform that supports mission critical solutions and applications, making them available to your organization when it needs them. Windows Server 2008 is the platform on which our customers can build their business on.
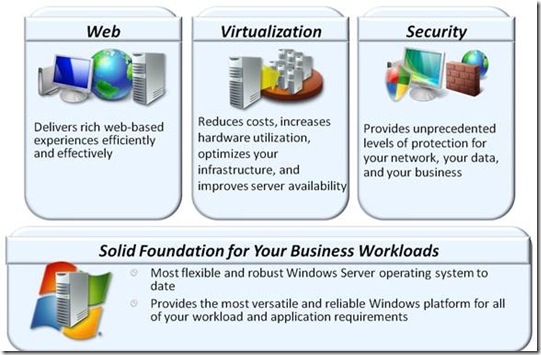
The Four Pillars of Windows Server 2008
Windows Server Platform – What’s New in Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server Virtualization (Hyper-V) : The Windows Server 2008 wave will include Windows Server Virtualization (Hyper-V), a powerful, performant, virtualization technology with strong management and security features. Windows Server virtualization will help businesses reduce costs, increase agility and system availability for production server consolidation, disaster recovery, test and development, and, when coupled with System Center Virtual Machine Manager, the end-to-end management of dynamic datacenters.
- A World-Class Web and Applications Platform: Windows Server 2008 provides a secure, easy-to-manage platform for developing and reliably hosting applications and services that are delivered from the server or over the Web. New features include simplified management, increased security, and both performance and extensibility improvements which delivers a unified platform for Web publishing that integrates Internet Information Services 7.0 (IIS7), ASP.NET, Windows Communication Foundation, and Microsoft Windows SharePoint Services.
- Improved Networking Performance: Windows Server 2008 introduces the biggest change in the networking stack since Windows NT 4.0. Technologies like Receive Window Auto-tuning, Receive Side Scaling, and Quality of Service (QOS) allow organizations to take full advantage of today's multi-Gigabit networks. Integrated IPsec and the new Windows Firewall with Advanced Security allow organizations to completely secure and control the flow of network traffic.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance: Windows Server 2008 has been developed from the ground up with the strictest security in mind. Always "shields up," Windows Server 2008 installs only the needed services for the roles the server is performing. Enhanced auditing, Drive Encryption, event forwarding, and Rights Management Services are just some of the technologies that help organization adhere to today's strict IT compliance standards.
- Take Back Control Over Your Remote Infrastructure: Managing servers, services, and security at remote locations is an on-going challenge for IT Professionals. Windows Server 2008 simplifies administration of the servers in branch offices with enhancements to Active Directory, including Read-Only Domain Controllers and administrative role separation. Technologies like BitLocker and the Server Core installation option are specific features that increase security and address the unique needs of branch offices.
- Server Management Made Easier: Simplifying the day-to-day complexities of server administration is a key theme in many of the enhancements included in Windows Server 2008. New management tools like the Server Manager Console provides a single, unified console for managing a server's configuration and system information, displaying server status, identifying problems with server role configuration, and managing all roles installed on the server.
- Enhanced Scripting and Task Automation: New technologies like Windows PowerShell, a command-line shell and scripting language, helps IT Professionals automate common tasks. With a new admin-focused scripting language, more than 120 standard command-line tools, and consistent syntax and utilities, Windows PowerShell allows IT professionals to more easily control system administration and to accelerate automation.
- Presentation Virtualization: With Windows Sever 2008, users will have secure access to internal applications through firewall-friendly ports. With Windows Server Terminal Services RemoteApp, only the application window, not the entire remote desktop, launches and runs in its own resizable, interactive window on the client computer's desktop.
- Protect Unhealthy Computers from Entering the Network: Network Access Protection (NAP) addresses the industry-wide problem of unhealthy computers accessing and compromising an organization's network. NAP is used to ensure that any computer connecting to the network meets corporate policy for "healthy" requirements, to limit network access for computers not meeting the predefined policy, providing remediation services to get those computers back to a healthy state, and to provide ongoing compliance-checking.
- Better Together with Windows Vista: Because Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 are built as part of a single development project, they share a number of new technologies across networking, storage, security and management. Organizations will immediately see the benefits of running Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista as their client and server solution.